Stack Buffer Overflow
Introduction
A stack buffer overflow is a severe software vulnerability that occurs when a program writes more data to a buffer on the stack than the allocated memory can hold. This leads to memory corruption, which may allow attackers to execute arbitrary code, crash the program, or exploit the underlying system. Understanding how stack buffer overflows occur and implementing proper mitigation techniques is vital for secure software development.
How Stack Buffer Overflow Works
1. Stack Basics
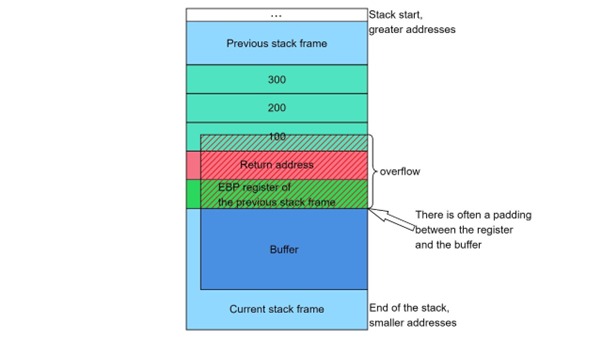
The stack is a region of memory that manages function calls, stores local variables, and holds control flow data such as return addresses. Each time a function is called, a stack frame is created containing:
- Local variables
- Arguments
- Return address
This makes the stack a prime target for attackers.
2. Buffer Overflow Mechanism
- Buffer Allocation: Buffers (like character arrays) are allocated on the stack to store user input or temporary data.
- Data Overflow: If the program fails to validate the input size, an attacker can provide more data than the buffer can handle.
- Memory Corruption: Overflowing the buffer causes excess data to overwrite adjacent memory, including crucial data like the return address or function pointers.
3. Exploitation Process
- Malicious Input Crafting: The attacker crafts input designed to overwrite critical stack data.
- Return Address Overwrite: Overwriting the return address redirects the program’s control flow.
- Code Execution: When the function returns, control is transferred to the attacker’s code, allowing arbitrary code execution or system compromise.
Preventing Stack Buffer Overflows
1. Bounds Checking
- Validate input sizes before writing to buffers.
- Use safe functions like
strncpy()instead of unsafe ones likestrcpy().
2. Compiler Protections
- Stack Canaries: Insert random values between buffers and control data to detect corruption before function returns.
- ASLR (Address Space Layout Randomization): Randomizes memory addresses, making it difficult for attackers to predict memory layout.
- DEP (Data Execution Prevention): Prevents code execution in non-executable memory regions, thwarting malicious code execution.
3. Avoid Unsafe Functions
- Avoid using functions like
gets()andstrcpy()that don't enforce buffer boundaries and are prone to overflow.
4. Modern Language Features
- Use programming languages such as Python, Java, or Rust, which handle memory management automatically and provide strong safety guarantees.
Conclusion
Stack buffer overflow vulnerabilities have been responsible for some of the most critical security breaches in computing. Developers must understand the causes of these vulnerabilities and implement preventive measures such as input validation, safer coding practices, and enabling compiler-based security features. By following best practices and utilizing modern development tools, developers can reduce the risks associated with stack buffer overflows and create more secure software.
Visual Aid
You can use absolute paths to reference images located in the static directory: